Understanding Radiation Therapy: What You Need to Know
Radiation therapy, often referred to as radiotherapy, is a powerful treatment used to fight various types of cancer. It uses high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells, while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. While the idea of radiation can sound daunting, it is one of the most common and effective treatments for many cancers. In this article, we’ll explore how radiation therapy works, its common side effects, and share a real-life example of a patient’s experience with this treatment.
How Radiation Therapy Works
Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells. When the DNA of a cancer cell is damaged, it can no longer grow or divide, causing the cell to die. Radiation can be delivered from outside the body (external beam radiation) or from within the body (internal or brachytherapy).
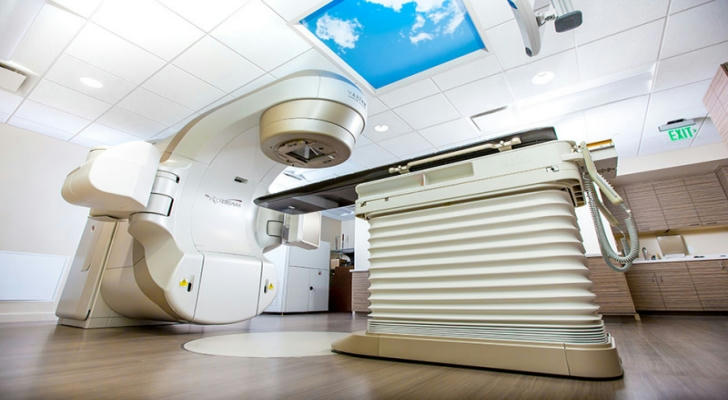
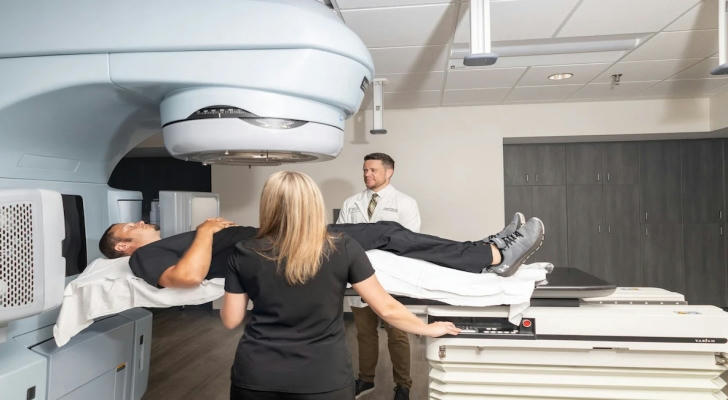
External Beam Radiation
In external beam radiation therapy, a machine called a linear accelerator directs beams of high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation at the tumor. This is a non-invasive procedure where the patient typically lies on a treatment table, and the machine is positioned around them. The process is painless and typically lasts only a few minutes per session.
Internal Radiation (Brachytherapy)
In internal radiation therapy, radioactive material is placed directly inside or very close to the tumor. This method is often used for cancers of the prostate, cervix, or uterus. Because the radiation is placed directly at the source, it can deliver higher doses of radiation to the tumor while minimizing the exposure to surrounding healthy tissue.
Systemic Radiation
This form involves radioactive substances that are administered orally or by injection. These substances travel through the bloodstream to target cancer cells, often used for certain types of thyroid cancer or to treat bone cancer.
Common Side Effects of Radiation Therapy
While radiation therapy is effective in treating cancer, it can also cause side effects, as the treatment may affect both healthy and cancerous cells. The type and severity of side effects depend on the area of the body being treated, the dose of radiation, and the patient’s overall health. Some of the common side effects include:
Fatigue
One of the most common side effects of radiation therapy is fatigue. Patients often report feeling very tired, even after adequate rest. This fatigue tends to develop gradually during the course of treatment and can last for weeks or even months after treatment ends.
Skin Irritation
When radiation is applied to the skin, it can cause redness, dryness, or irritation similar to sunburn. In some cases, the skin may peel or blister. Special lotions and care instructions can help manage skin side effects.
Hair Loss
Radiation therapy can cause hair loss in the area being treated. For example, if radiation is used on the head, patients may experience hair loss on their scalp. However, hair usually grows back once treatment is complete.
Nausea and Vomiting
Depending on the area of treatment, radiation can cause nausea and vomiting, especially if the abdomen or pelvis is being treated. Medications are often prescribed to help manage these symptoms.
Long-Term Effects
Some side effects of radiation may appear months or years after treatment. These can include issues like lymphedema (swelling in the limbs), changes in fertility, or secondary cancers in rare cases.
Real-Life Example: Sarah’s Journey with Radiation Therapy
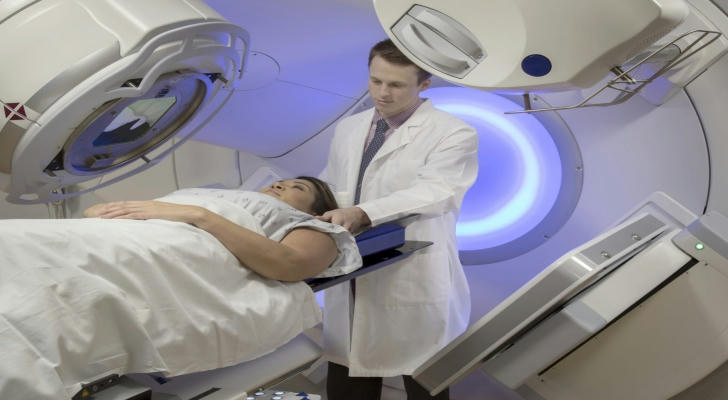
Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, was diagnosed with breast cancer. After undergoing surgery to remove the tumor, her oncologist recommended radiation therapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
During her treatment, Sarah experienced fatigue and skin irritation, which made her feel self-conscious, but her healthcare team was always there to help her manage these side effects. The radiation therapy was targeted precisely at the tumor site, so Sarah was able to continue with her daily activities, though she found herself needing more rest than usual. Despite the temporary side effects, Sarah was grateful for the treatment, as it successfully minimized the risk of the cancer returning.
One year after completing her radiation therapy, Sarah is cancer-free and back to enjoying her normal routine. Her experience with radiation therapy wasn’t easy, but she was able to manage the side effects with the support of her medical team, and the results were life-saving.
Why Radiation Therapy Is Important
Radiation therapy is an essential tool in the fight against cancer. It can shrink tumors, kill cancer cells, and prevent cancer from spreading. It is often used in combination with other treatments like surgery and chemotherapy for a more comprehensive approach to cancer treatment. In many cases, radiation therapy can be the difference between cancer remission and recurrence.
In some cases, radiation therapy is used as the primary treatment for certain types of cancer, such as prostate, brain, or head and neck cancers. For others, it may be used to reduce symptoms or to treat cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as bone or brain metastases.
Conclusion
Radiation therapy is a powerful and effective cancer treatment that helps many patients recover and regain their quality of life. While side effects are a common part of the process, they are often temporary and manageable with the right care. If you or a loved one is undergoing radiation therapy, it’s important to understand both the benefits and challenges of the treatment.
With the right medical team, resources, and support, patients can navigate the journey of radiation therapy and emerge stronger. Early intervention, precision in targeting tumors, and post-treatment care are all key to achieving the best outcomes. If you’re undergoing radiation therapy or considering it as part of your cancer treatment plan, talk to your healthcare provider about how to manage any side effects and make the treatment process as smooth as possible.
