The Importance of Portable Blood Glucose Monitors for Diabetics
Diabetes management is a critical aspect of living with this chronic condition, affecting millions of individuals in the United States. One of the most essential tools for managing diabetes is the portable blood glucose monitor, commonly known as a glucometer. These devices play a vital role in helping diabetics maintain their health by providing real-time data on blood sugar levels, enabling informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
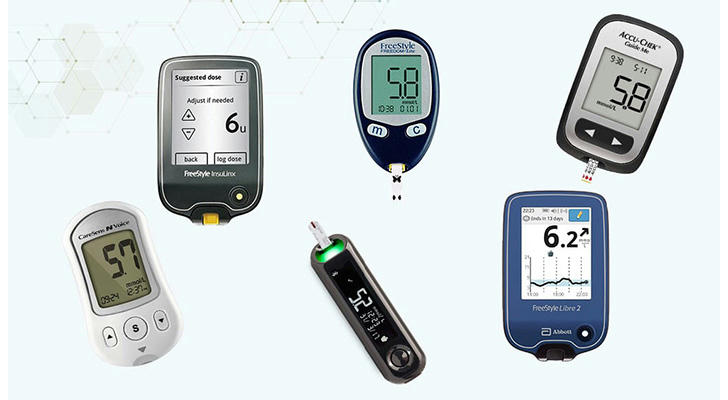
Understanding Blood Glucose Monitoring
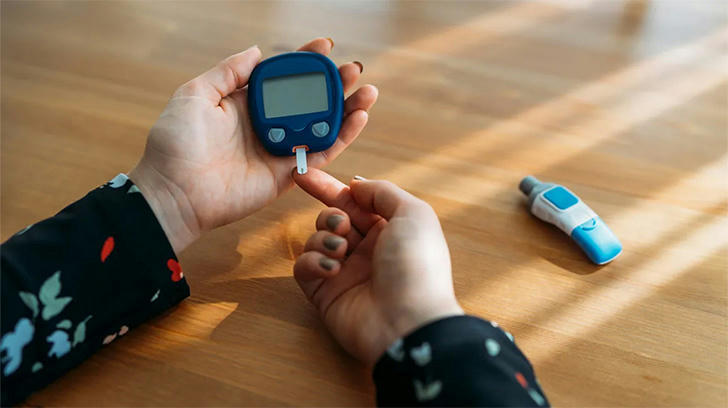
Blood glucose monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it helps track how various factors—such as food intake, physical activity, and medications—affect blood sugar levels. By regularly checking their glucose levels, diabetics can better understand their condition and make necessary adjustments to their management plans. Portable blood glucose monitors allow users to measure their blood sugar levels conveniently and accurately, often using just a small drop of blood from a fingertip.
Benefits of Portable Blood Glucose Monitors
Real-Time Data: Portable blood glucose monitors provide immediate feedback on blood sugar levels. This real-time data is essential for making quick decisions regarding food intake or insulin administration. For instance, if a reading indicates low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), individuals can take corrective actions immediately by consuming fast-acting carbohydrates.
Empowerment and Independence: Having access to a portable monitor empowers diabetics to take control of their health. They can test their blood sugar levels at home, work, or while traveling without needing to visit a healthcare facility. This independence fosters confidence in managing their condition.
Trend Analysis: Many modern portable monitors come equipped with memory functions that allow users to track their glucose readings over time. By analyzing these trends, diabetics can identify patterns related to diet, exercise, and medication efficacy. This information is invaluable when discussing treatment plans with healthcare providers.
Reduced Complications: Regular monitoring helps prevent complications associated with poorly managed diabetes. By keeping blood sugar levels within target ranges, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications such as neuropathy, kidney disease, and cardiovascular issues.
Convenience: Portable monitors are designed for ease of use. Most devices are compact and lightweight, making them easy to carry in a pocket or bag. This portability encourages more frequent monitoring, which is essential for effective diabetes management.
Types of Portable Blood Glucose Monitors
There are several types of portable blood glucose monitors available on the market today:
Traditional Glucometers: These devices require users to prick their fingers to obtain a blood sample. The sample is placed on a test strip inserted into the meter, which provides a reading within seconds.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): While not strictly portable glucometers in the traditional sense, CGMs offer continuous monitoring of glucose levels through sensors placed under the skin. They provide real-time data and alerts for high or low blood sugar levels but may require periodic calibration with traditional glucometers.
Flash Glucose Monitors: Similar to CGMs, flash monitors allow users to scan a sensor worn on the body to obtain glucose readings without finger pricks. This technology offers convenience and ease of use while still providing valuable data for diabetes management.
Challenges and Considerations
While portable blood glucose monitors offer significant benefits, there are challenges associated with their use:
Cost: Some devices and test strips can be expensive, leading to financial barriers for some patients. Insurance coverage varies widely, impacting access to these essential tools.
Accuracy: Although most modern monitors are reliable, discrepancies can occur between different devices or between device readings and laboratory results. Users should regularly calibrate their devices according to manufacturer instructions.
Education: Proper education on how to use these devices effectively is crucial for accurate readings and effective diabetes management. Healthcare providers play an essential role in training patients on using their monitors correctly.
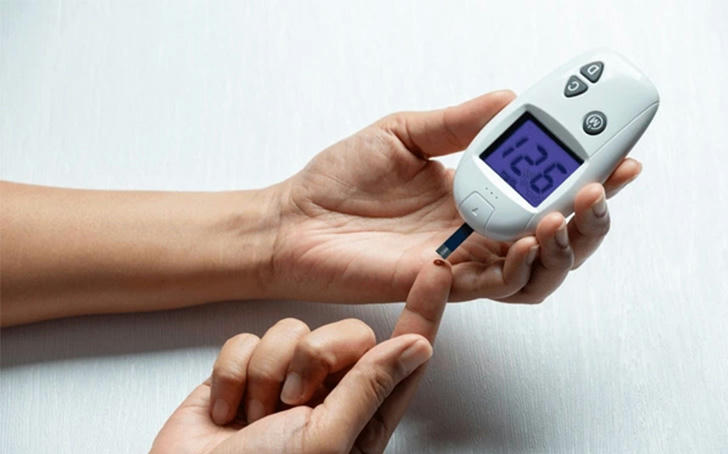
Conclusion
Portable blood glucose monitors are indispensable tools for individuals living with diabetes in the United States. They provide critical real-time data that empowers users to manage their condition effectively and make informed decisions about their health. The convenience and accessibility of these devices contribute significantly to improved health outcomes and quality of life for diabetics.
As technology continues to advance, the future of diabetes management looks promising with innovations such as continuous glucose monitoring systems that integrate seamlessly into daily life. Ultimately, regular monitoring through portable blood glucose devices not only helps prevent complications but also enhances overall well-being for those living with diabetes.
