Early Warning Signs of Heart Disease You Shouldn’t Ignore
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, but it often starts with subtle symptoms that can easily go unnoticed. Recognizing these early warning signs is crucial for seeking timely medical care, managing the condition, and reducing the risk of life-threatening complications. This article highlights the key early symptoms of heart disease, risk factors, and shares a real-life example to help you understand the importance of early detection.
Common Early Symptoms of Heart Disease
The symptoms of heart disease can vary depending on the specific condition, such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, or arrhythmia. However, some common warning signs often precede major cardiac events:
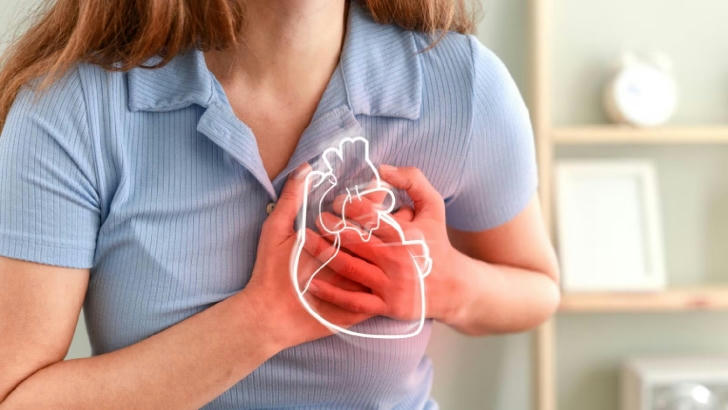
Chest Discomfort or Pain
A classic symptom of heart disease is chest pain or discomfort, often described as pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation. This is a potential sign of angina, which occurs when the heart doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. While not always severe, it should never be ignored.
Shortness of Breath
If you experience difficulty breathing during routine activities or while lying down, it may indicate an issue with your heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently. Shortness of breath is a common early sign of heart failure.
Fatigue or Weakness
Persistent fatigue, even after adequate rest, can signal an underlying heart problem. The heart may struggle to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, leaving you feeling drained.
Swelling in the Legs, Ankles, or Feet
Fluid retention, often seen as swelling (edema) in the lower extremities, can indicate heart failure. This occurs when the heart’s weakened pumping function causes blood to back up in the veins.
Irregular Heartbeat
Feeling that your heart is racing, skipping beats, or beating too slowly could point to arrhythmia, a condition involving abnormal heart rhythms. This symptom should be evaluated promptly by a doctor.
Dizziness or Lightheadedness
Sudden dizziness or fainting may be a sign of a heart condition affecting blood flow. It can occur due to arrhythmias or narrowing of blood vessels.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing heart disease. Understanding these risk factors can help you assess your personal risk and take preventive measures:

Family History: If close relatives have a history of heart disease, your risk is significantly higher.
Age: Risk increases as you grow older, especially after age 45 for men and 55 for women.
Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol: These conditions strain the heart and contribute to plaque buildup in arteries.
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart.
Poor Diet and Lack of Exercise: An unhealthy lifestyle can lead to obesity and other risk factors for heart disease.
Real-Life Example: John’s Story

John, a 52-year-old accountant, was leading a relatively sedentary lifestyle, with long hours at work and little physical activity. Over time, he started noticing unusual fatigue, even after a good night’s sleep. He also experienced occasional chest discomfort, especially after climbing stairs, but dismissed it as indigestion.
One morning, John felt lightheaded and short of breath while walking his dog. Concerned, he visited his doctor, who performed an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood tests. The results revealed that John had significant coronary artery disease. His doctor explained that plaque buildup in his arteries was restricting blood flow to the heart.
Fortunately, John sought medical attention before a major cardiac event occurred. He underwent a minimally invasive procedure to improve blood flow and adopted a heart-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise. With these changes, John significantly reduced his risk of future heart complications.
Why Early Detection Matters
Early diagnosis of heart disease can make a significant difference in outcomes. Many heart conditions can be managed or even reversed with lifestyle changes, medications, or medical procedures. Ignoring symptoms increases the risk of a heart attack, stroke, or chronic heart failure, which can have life-altering consequences.
If you notice symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or persistent fatigue, don’t wait to see if they improve on their own. Prompt evaluation by a healthcare provider can help you address the issue before it becomes more serious.
Conclusion
Heart disease is a serious condition, but recognizing its early signs and taking proactive steps can greatly improve your prognosis. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned or have risk factors for heart disease, consult a healthcare provider for an evaluation. Prevention and early intervention are your best tools for maintaining a healthy heart and a longer, more active life. Don’t delay—your heart deserves the care it needs.
